|
Earth Observation Laboratory
Function:
To observe the Earth:-
Weather
Geology
Agriculture
Pollution
Oceans
Vegetation
Atmosphere
House sensors - Radar, infra-red, photographic, radio, magnetic

 This
image is from the Skylab missions, and shows the United Kingdom
- a rare site without cloud cover. This is the sort of view that
you would get with the naked eye. Extremely good close-up images
are now available commercially that show objects as little as
half a metre across (20 inches). Also, cameras look at other wave
lengths, such as in the infra red, so detail shows up that is
not visible to the eye. Radar is also used to monitor sea conditions.
It can measure the height of waves accurately to within a few
centimetres or inches. Wind speeds can also be measured using
doppler radar, and back on the ground, computer enhancement can
reveal geological information that cannot be found at ground level. This
image is from the Skylab missions, and shows the United Kingdom
- a rare site without cloud cover. This is the sort of view that
you would get with the naked eye. Extremely good close-up images
are now available commercially that show objects as little as
half a metre across (20 inches). Also, cameras look at other wave
lengths, such as in the infra red, so detail shows up that is
not visible to the eye. Radar is also used to monitor sea conditions.
It can measure the height of waves accurately to within a few
centimetres or inches. Wind speeds can also be measured using
doppler radar, and back on the ground, computer enhancement can
reveal geological information that cannot be found at ground level.
One of the many unexpected results of entering the space era, was the discovery of how useful Earth observation from space could be. Aerial photographs had been used to good effect, but the view from orbit opened up many more possibilities. Something that started as a way of keeping an eye on what neighbouring countries were doing, became an essential tool.
It has provided:
- hurricane and typhoon warnings
- monitoring of global weather patterns
- evidence of environmental problems, including
- oil spillages
- forest fires
- deforestation
- desert growth
- ozone layer depletion
- El Nino phenomenon
Earth Observation has been used extensively for
- mineral resources prospecting
- monitoring crop condition
- oceanographic study
The use of satellite images for today's weather forecasts is now taken for granted by most of us.
Project:
Identify these images and the features in them.

1 -- a) New York Skyscaper b) A Pyramid at Giza c) The end of a key

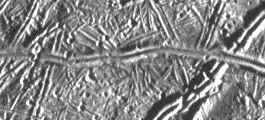
2 -- a) Ice on Europa b) Highways in Canada in winter c) Scratches on a metal plate


3 -- a) A river valley in the Argyre Basin on Mars. b) Trenches in France in 1917 c) Surface of a biscuit


4 -- a) The asteroid Mathilda b) A potato c) A boulder from the Gobi Desert


5 -- a) Paris b) The docking port on the Mir Space Station c) Part of a printed circuit board


6 -- a) Mars, Ares Valley river out flow b) Canyons and dried up rivers in the Mojave Desert c) Sand on a tray

Answers 1 b, 2 a, 3 b, 4 a, 5 a, 6 c

To download images from space go to Terra Server Images from space

Go
to Space Station 2020 Specification
Return
to title page

|













